What is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash? – Part 5: Use Case Showdown

Explore the Full Series of
“What is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash?”
In this final installment of our series, we undertake a thorough exploration of the distinctive applications and functionalities that distinguish Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash. Our focus spans key categories, including currency, savings, tokens, decentralized finance (DeFi), and privacy; with the aim of unraveling the unique attributes each cryptocurrency contributes to these domains.
The underlying value of a cryptocurrency lies in its utility, shaped by diverse use cases that empower users to engage in activities they deem valuable. As we delve into the exploration and comparison of BTC and Bitcoin Cash, we aim to illuminate the various facets and applications that afford users financial freedom in the digital realm.
Table of Contents:
BCHFAQ Flipstarter - Phase 2
Join the Bitcoin Cash Revolution: Fund More Informative Content on BCHFAQ
Currency
Cryptocurrencies are engaged in a competitive race to establish themselves as the premier digital currency, with a benchmark set by traditional currencies. To be considered an ideal currency, certain fundamental properties must be met. These include fungibility, durability, portability, recognizability, and stability.
Fungibility is a crucial characteristic implying that each unit of the currency is interchangeable and identical, ensuring that every unit has the same value as any other unit. In essence, fungibility ensures the seamless and equal exchange of currency units, without any differentiation.
Durability refers to the ability of the currency to withstand wear and tear over time. In the context of cryptocurrencies, durability translates to the resilience of the underlying technology and the resistance to potential vulnerabilities that could compromise the integrity of the currency.
Portability is a measure of how easily the currency can be transported or transferred between parties. Cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology to enhance portability, theoretically allowing for swift and borderless transactions, irrespective of geographical distances.
Recognizability underscores the importance of easily identifying and verifying the authenticity of the currency. In the cryptocurrency realm, this property relates to the clarity and transparency of transaction histories, ensuring that each unit can be traced through the blockchain and validated.
Stability is a pivotal factor for any currency, emphasizing the need for a consistent and predictable value over time. A stable currency minimizes the impact of volatility, providing users with confidence in its purchasing power.
Now, let’s examine how BTC and Bitcoin Cash compare in these fundamental properties.
Currency Conundrum
BTC is grounded in the theoretical principle of fungibility, suggesting that each unit is interchangeable with any other. However, concerns arise due to the blockchain’s traceability, allowing governments and other malicious actors to monitor activity. Despite the blockchain’s pseudonymity, analysis tools can potentially link funds with identities, impacting the fungibility of coins, especially if specific transactions face discouragement or penalties. The absence of cost-effective coin mixing options (discussed in more detail below), due to high fees, raises the possibility that certain units of BTC may not attain complete fungibility with all others.
On the durability front, BTC has proven itself as a stalwart. Confirmed transactions are, for all intents and purposes, permanent. Additionally, the network boasts an impeccable track record, having never experienced any downtime since its inception.
Of course, the durability of a currency hinges on its ability to endure well into the future. This remains an open question for all cryptocurrencies, BTC included. Currently, BTC’s protocol has experienced a considerable degree of stagnation. Adopting such a strategy poses a significant risk in a digital landscape characterized by continual advancements and adaptations to meet evolving user demands. Should BTC fail to adequately address the evolving needs of its user base, the ossification in its development approach may prove to be a haunting vulnerability.
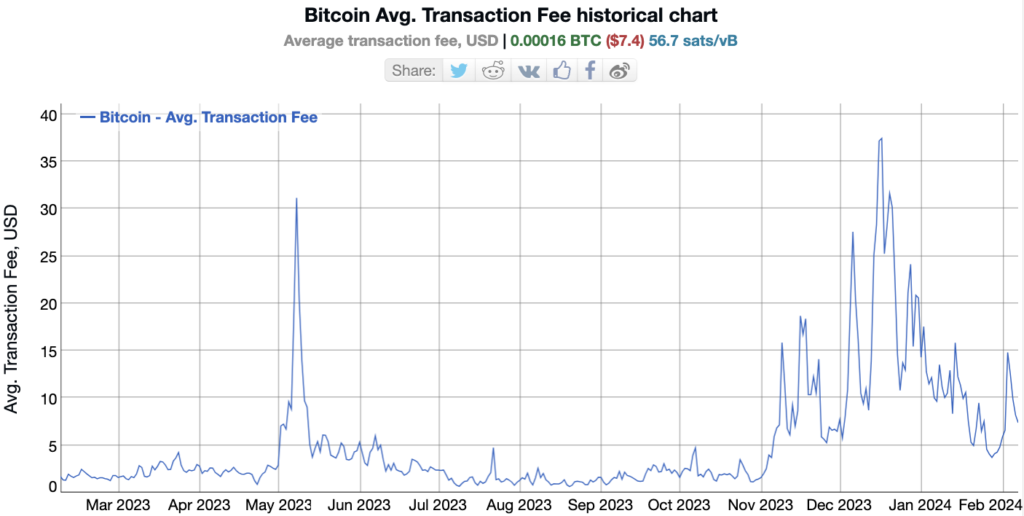
BTC faces a significant challenge in terms of portability, primarily due to very high transaction fees and the widespread adoption of Replace-by-Fee (RBF). High transaction fees make it very expensive to transact. This particularly impacts Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs) of small values where the fees can eat up a large percentage of the UTXO amount. In fact, many of the smallest UTXOs are effectively stuck permanently, as the fee to move them would be larger than the amount to be moved. These fee issues negatively affect the overall portability quality of BTC.
RBF introduces a level of uncertainty by making transactions difficult or impossible to settle until they are confirmed into a block. The possibility of RBF transactions being sent back to the receiver adds a layer of complexity, preventing BTC from achieving instant transferability. In this aspect, BTC falls short when compared to the perception of traditional currencies, as the finality of transactions involving BTC cannot be guaranteed until after confirmation. And confirmation usually takes several minutes, even without the competition for transaction inclusion on the network. In the case of intense transaction fee competition, transactions can take days or weeks to confirm.
Even on the Lightning Network, which was envisioned as BTC’s second-layer scaling solution to enhance portability, users encounter many issues. Reports indicate that portability problems persist within the Lightning Network, with users often facing difficulties in routing transactions. These challenges further underscore the limitations of BTC’s current infrastructure in achieving the seamless and instantaneous transferability desired for a widely adopted digital currency.
Recognizability is a strong suit for BTC as long as users employ legitimate wallet software. The transparency of the blockchain ensures that every unit of BTC can be meticulously accounted for, contributing to the overall recognizability of the cryptocurrency.
On the stability front, BTC grapples with high volatility, rendering it inherently unstable in terms of its value. The unpredictable fluctuations in value have implications for its role as a stable currency, attracting both enthusiasts and skeptics in ongoing discussions about the future trajectory of BTC in the payments landscape.
Cash is King
Bitcoin Cash distinguishes itself by maintaining fungibility even for UTXOs supposedly “tainted” in the eyes of governments, as transactions on the network are characterized by their extreme cost-effectiveness. The affordability of transactions, coupled with privacy-enhancing solutions like CashFusion (discussed in more detail below), poses challenges for governments attempting to breach fungibility. This low-cost privacy mechanism contributes to the overall robustness of fungibility within the Bitcoin Cash ecosystem.
Similar to BTC, Bitcoin Cash boasts durability as a key feature. The network operates without any downtime, and confirmed transactions are extremely unlikely to be reversed, all but ensuring the security and permanence of transactions.
Like BTC, Bitcoin Cash’s ability to sustain operations far into the future is uncertain, leaving its ultimate durability in doubt. However, with a history marked by an active and dynamic development path, the Bitcoin Cash community demonstrates a strong commitment to ongoing adaptation and evolution. This dedication alleviates concerns about meeting market demand over extended time frames, positively impacting its quality of durability.
Portability emerges as a notable strength for Bitcoin Cash, facilitated by its dedication to sub-cent fees. The cost-effectiveness of transactions, due to the careful use of larger blocks, ensures that virtually every transaction is promptly included in a block. This reliability of unconfirmed transactions as a form of payment enhances the overall portability of Bitcoin Cash, allowing for transactions to be considered final right away in most cases.
Recognizability is on par with BTC, as Bitcoin Cash-compatible wallet software automatically verifies the authenticity of transactions. This seamless verification process contributes to the user-friendly experience and widespread recognizability of Bitcoin Cash.
However, similar to BTC, Bitcoin Cash is not immune to the challenges of high volatility. The inherent fluctuations in value underline the broader cryptocurrency market dynamics, prompting ongoing discussions about the role of Bitcoin Cash as a means of exchange within the digital economy.
Key Takeaway:
In the competitive realm of digital currencies, the pursuit of premier status as a true currency revolves around fundamental properties like fungibility, durability, portability, recognizability, and stability. BTC faces challenges with practical fungibility due to a lack of low-cost privacy options. BTC portability issues arise from high transaction fees, Replace-by-Fee policies, and Lightning Network limitations. Both coins struggle with stability due to extreme market volatility. Up to the present, both BTC and Bitcoin Cash have very high durability, but questions remain about their ability to endure into the far future – particularly BTC and its ossified protocol. While recognizability is not an issue for either coin, Bitcoin Cash excels in portability and fungibility due to low-cost transactions and extremely affordable privacy options.
Savings
The Bitcoin whitepaper expressed a desire for the coin to serve as peer-to-peer cash. Cash, in its most useful form, should provide the ability to save and store wealth. Historically, an asset must first be a medium of exchange before it can become a good store of value.
Cryptocurrencies are still in their infancy. Therefore, since BTC and Bitcoin Cash are still evolving their medium-of-exchange functionality, we shouldn’t expect optimum store-of-value properties. Both coins are highly volatile, which introduces a lot of risk into storing wealth using either one. We covered this briefly in the previous section, but we’ll explore more here.
Store-of-Value Victory
BTC, over its lifetime, has predominantly experienced appreciation in value. An examination of its price history at the time of writing reveals that approximately 98% of BTC’s historical prices have been below the current price of $49,697 (12 Feb 2024). This statistical insight implies that acquiring BTC during the vast majority of its existence would provide the opportunity to realize gains today.
These facts instill confidence in BTC as a robust financial asset. Its current price, not terribly far from all-time highs, provides a reassuring sense of security for individuals looking to allocate a portion of their savings to the cryptocurrency.
Moreover, boasting a market capitalization surpassing that of all other individual coins in the space, Bitcoin naturally garners substantial attention. The availability of BTC exchange-traded funds (ETFs) further expands the avenues for consumer participation in BTC investing, enhancing accessibility and facilitating a broader adoption of the cryptocurrency.
Yet, it’s essential to underscore that past performance does not guarantee future returns. Growing network congestion, escalating fees, and ongoing contention surrounding BTC’s development trajectory introduce uncertainties about its enduring viability as a wealth storage asset.
While cryptocurrencies have achieved widespread recognition, the actual user and investor base remains comparatively limited. Given BTC’s current user capacity constraints, the long-term value of Bitcoin in a scenario where the mass market demands direct access to cryptocurrency remains uncertain. This potential future would surely unveil numerous surprises within the crypto landscape and BTC risks getting left behind by more adaptable currencies.
Hedging Haven
Bitcoin Cash shares a historical lineage with BTC, including their price history before the split on 1 Aug 2017. An examination of Bitcoin Cash’s price history at the time of writing reveals that approximately 58% of its historical prices have been below today’s price of $286 (12 Feb 2024). That means that a purchase of pre-split Bitcoin (keeping the resulting Bitcoin Cash) or post-split Bitcoin Cash on any random day since the beginning provides a decent chance of realizing a gain today.
Clearly Bitcoin Cash’s current track record in terms of its price is inferior to BTC’s upward trend. However, Bitcoin Cash has a trick up its sleeve. General Protocols, a Bitcoin Cash-based company developing smart protocols, introduces a unique element to savings through BCH Bull. Leveraging the AnyHedge protocol, BCH Bull enables users to either enter a leveraged long position on Bitcoin Cash against another asset (e.g., USD, BTC, gold, silver) or utilize Bitcoin Cash to hedge value denominated in one of the other assets.
The focus here lies in the hedging aspect, allowing users to maintain stability for a specified amount. A user can use Bitcoin Cash to stabilize the value of $1,000 USD for 90 days, for example. Upon maturation of the hedging contract, the user will receive $1,000 worth of Bitcoin Cash no matter how the price moved during the interim. On top of that, users may earn a premium just to hedge, paid for by the other party – the speculator. All this happens on-chain and non-custodially.
With this service, Bitcoin Cash presents an innovative solution for saving value in terms of popular assets, mitigating concerns associated with volatility. The volatility of the underlying asset no longer has to impede one’s ability to use it as a savings vehicle. In the near future it may become possible to tokenize the hedged positions, allowing for on-chain, smart contract-based stablecoins denominated in various assets, further diversifying Bitcoin Cash-based savings options.
Key Takeaway:
The concept of savings in the realms of BTC and Bitcoin Cash is intricately tied to their paths toward becoming mediums of exchange, which are still in their initial stages. While both coins aspire to serve as stores of wealth, their current volatility introduces risks into saving money using either currency. Examining their historical price trends, BTC has predominantly experienced appreciation, but uncertainties arise due to network congestion and contentions concerning development. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash has experienced less favorable historical returns. However, Bitcoin Cash provides a savings solution – BCH Bull, utilizing the AnyHedge protocol. This service empowers users to either enter leveraged long positions or hedge value on-chain, introducing a unique approach to stabilizing wealth denominated in assets such as USD, BTC, precious metals, and more. Bitcoin Cash, through such innovations, emerges as a platform offering innovative solutions for saving value in popular assets, addressing concerns related to volatility.
Tokens
Tokens operating on cryptocurrency platforms play a pivotal role in expanding the utility and functionality of blockchain networks. These tokens serve as digital assets, representing a diverse array of functionalities within the decentralized ecosystem. They act as representative assets, symbolizing ownership or stake in a particular project, platform, or decentralized application.
Beyond mere financial instruments, tokens are leveraged as voting shares, enabling token holders to participate in governance and decision-making processes, fostering a decentralized and inclusive approach to network management. Moreover, tokens play a crucial role in smart contract applications, facilitating programmable and self-executing agreements. These programmable tokens enable the automation of various processes, ranging from tokenized assets and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to the creation of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that represent ownership of digital or physical assets.
Let’s explore how BTC and Bitcoin Cash have implemented token standards and see how they compare.
Token Taboo
BTC has historically refrained from incorporating a native token standard into its base layer. During the consideration of colored coins by Counterparty and other platforms, BTC developers imposed restrictions on adding arbitrary data to the blockchain, significantly curtailing the feasibility of token layers at that juncture.
Although Counterparty later introduced a token standard utilizing the OP_RETURN field in BTC transactions, the infrastructure and validation required for such token functionality operate independently from the actual BTC network. Consequently, Counterparty-based tokens do not reside directly on the BTC blockchain itself.
While token schemes like RGB and Taro emerged on BTC’s Lightning Network in recent years, their adoption has been severely limited, likely influenced by the challenges related to liquidity and routing on the Lightning Network.
Despite the subdued reception of token schemes on the Lightning Network, one particular token standard within the BTC ecosystem has garnered significant attention. Through a workaround that exploits certain features introduced by the SegWit and Taproot upgrades, a novel token layer, commonly known as Ordinals, has been developed.
BTC ordinals and inscriptions offer innovative ways to store text, images, and diverse data on the blockchain. Ordinals act as serial numbers, assigning unique identifiers to units known as “satoshis” (equivalent to 0.00000001 BTC) in the order they were mined. Inscriptions are data attached to specific satoshis. The resulting tokens are not native to the base layer of BTC as they rely on third-party indexers to decide which satoshis represent which data. Therefore, the tokens themselves do not receive the benefit of miner-enforced validation and security.
Since Ordinals were not intended to be a feature of BTC, they have sparked intense debate within the ecosystem. Advocates view them as a revolutionary and secure means of data storage, contributing to the development of digital collectibles known as artifacts. Detractors argue that ordinals deviate from BTC’s core purpose as a store of value and may lead to network congestion and increased transaction fees. In fact, during the first year of the Ordinals phenomenon, average transaction fees went up to $30 USD multiple times due to demand. Some have also pointed out that, due to the reliance on third-party indexers, the data in Ordinals is not secured by miners and may be manipulated by software bugs or bad actors.
Opponents of the popular tokens have discussed methods of possibly censoring Ordinals transactions and excluding them from the blockchain. Whether that can be done through node policies or a more aggressive network upgrade remains to be seen. For now, the Ordinals craze continues as many users seek tokens associated with the coin with the highest market cap, hoping they will increase in value over time.
Nascent Native Tokens
Bitcoin Cash, like BTC, did not have its own token standard after the 2017 split. However, the development of the Simple Ledger Protocol (SLP) soon followed, allowing arbitrary token metadata to be linked to specific Bitcoin Cash outputs – paralleling but preceding the eventual activation of Ordinals on BTC.
Like Ordinals, the SLP operated outside the Bitcoin Cash base layer, relying on third-party indexers to synchronize token data and manage the chain of ownership. While the SLP faced challenges with dependence on external indexers, its lessons proved invaluable, guiding developers toward refining protocols for improved, more trustless implementations.

In May 2023, after years of discussion, development, and building consensus, Bitcoin Cash upgraded to implement CashTokens. For the first time on an implementation of Bitcoin – the cryptocurrency that started it all – tokens were able to exist on the base layer of the blockchain. That means there are actual token primitives – fungible and non-fungible – in the Bitcoin Cash protocol itself. Tokens are therefore validated by miners and inherit the same level of security that native units of Bitcoin Cash have.
Beyond native tokens and typical use cases for fungible tokens and NFTs, CashTokens unlock a realm of possibilities by leveraging the robust smart contract capabilities inherent in the Bitcoin Cash protocol. This innovation allows CashTokens, just like Bitcoin Cash units, to utilize the full spectrum of scripting capabilities within the protocol, offering the potential to implement a diverse range of smart contracts akin to those in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) universe. Despite the need for rewriting EVM contracts under the UTXO framework, Bitcoin Cash’s superior scalability positions CashTokens as an enticing choice for many exciting applications.
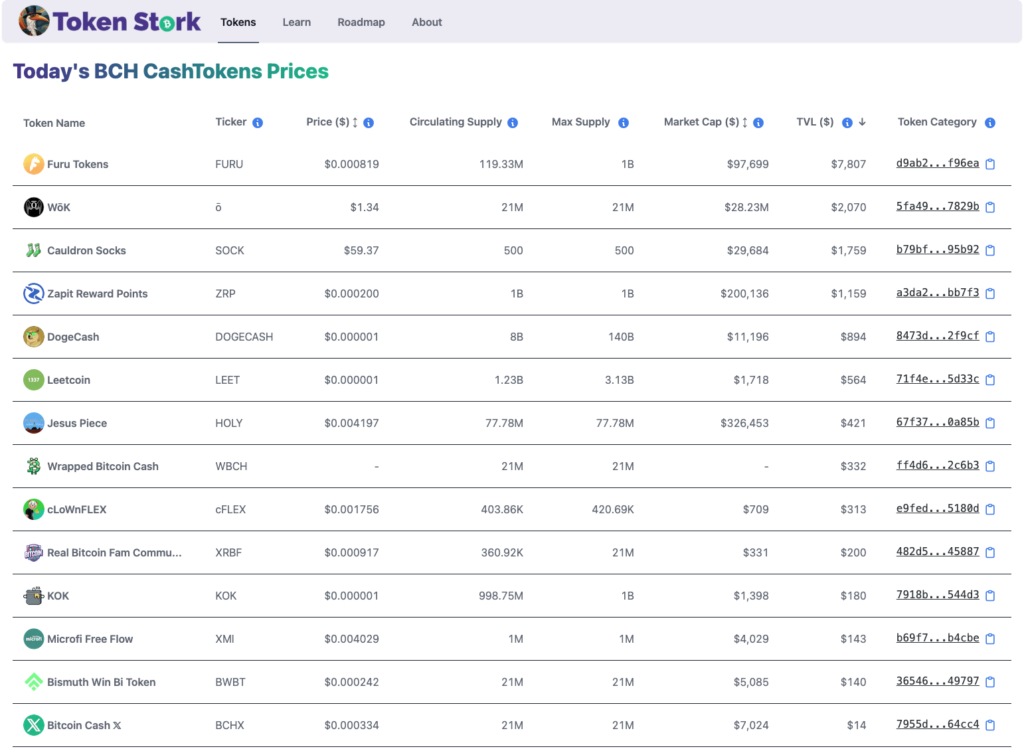
Token Stork provides a comprehensive listing of the thriving ecosystem’s most popular fungible CashTokens. While still in the early stages of the recent upgrade, some promising fungible token projects have already gained traction, such as Furu Tokens, Zapit Reward Points, and Dogecash.
TapSwap (discussed in more detail below) enables trading of the most sought-after non-fungible CashTokens, including BCH Gurus, Cash-Ninjas, and NFT tickets to the next Bitcoin Cash conference.
The process of initiating custom token projects on Bitcoin Cash has been significantly streamlined through the introduction of CashTokens Studio. This platform enables users to effortlessly mint both fungible and non-fungible tokens, allowing for the inclusion of logos and other essential metadata. For those with a more advanced understanding of token creation, developers can leverage an open-source minting contract, providing additional options for sophisticated token functionalities.
Key Takeaway:
The role of tokens in cryptocurrency platforms is pivotal, expanding the utility of blockchain networks beyond basic transactions. Tokens can act as representative assets, voting shares, and can facilitate smart contract applications, enabling programmable and self-executing agreements. BTC historically refrained from implementing a native token standard, leading to some pioneering developers exploiting aspects of BTC upgrades to create Ordinals. Ordinals offer innovative data storage but rely on third-party indexers. Additionally, they face questions over their alignment with BTC’s core purpose and concerns about network congestion. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash, after challenges with the mostly-deprecated Simple Ledger Protocol, introduced CashTokens. CashTokens allow fungible and non-fungible tokens to exist on the base layer with validation by miners, ensuring the same security as standard Bitcoin Cash transactions. CashTokens leverage the robust smart contract capabilities of the Bitcoin Cash protocol, allowing for diverse applications and scalability advantages over EVM chains. Despite its recent introduction, the CashTokens upgrade is already being leveraged by numerous projects to initiate compelling token ventures.
DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has emerged as a transformative force within the cryptocurrency space, reshaping traditional financial services by offering decentralized alternatives. In the context of BTC and Bitcoin Cash, exploring their DeFi options provides insights into the evolution of financial ecosystems built on these respective blockchains.
DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology to facilitate various financial services, including lending, borrowing, yield farming, and decentralized exchanges, without the need for traditional intermediaries. As BTC and Bitcoin Cash have had distinct evolutions since their split in 2017, their approaches to supporting DeFi applications differ. Understanding the nuances of DeFi offerings on BTC and Bitcoin Cash allows for a comprehensive comparison of their capabilities and contributions to the broader decentralized finance landscape.
DeFiance
For the last several years, dedicated proponents of BTC have been resistant to the concept of native DeFi options, deeming such features incongruent with the fundamental store-of-value characteristic they attribute to BTC. Simultaneously, developers working on BTC have shown little to no initiative over the years in enabling DeFi functionalities directly on the chain.
Consequently, the BTC blockchain lacks a dedicated DeFi infrastructure or options. The most optimistic scenario for BTC users involves resorting to cross-chain protocols like Thorchain or using wrapped BTC on an EVM chain, albeit with the caveat of centralized authority when employing asset wrapping services.
As of now, the prospect of native BTC DeFi faces uncertainty, with apparent lack of interest from both users and developers.
Redefining DeFi
Bitcoin Cash users and developers have expressed a longstanding interest in DeFi options, but the realization of required features faced delays due to distractions linked to community direction and challenges with the old reference node development team. These distractions have largely been resolved, paving the way for significant development progress over the past few years.
A pioneering example of native, on-chain DeFi for Bitcoin Cash emerged on memo.cash, a social media protocol built on the Bitcoin Cash blockchain. Through this platform, users gained the ability to engage in non-custodial buying and selling of SLP tokens. Although SLP activity has significantly decreased over time, this initiative provided Bitcoin Cash users with a glimpse into the potential possibilities of DeFi on the network.
In 2020, General Protocols, a Bitcoin Cash-focused company, unveiled the AnyHedge protocol. AnyHedge stands out as a decentralized financial solution featuring a transactional, collateral-based protocol that operates without systemic dependencies. Users engaged in AnyHedge contracts benefit from no exposure to counterparty risk, with contract details kept confidential until maturity. This protocol operates on-chain, eliminating the need for custodial involvement, and enables versatile and secure financial instruments.
Detoken, although now deprecated, played a pioneering role as the initial application to utilize the AnyHedge protocol. Detoken served as a dependable proving ground for AnyHedge, testing its capabilities and laying the groundwork for further development. In 2022, BCH Bull introduced the beta version of their novel AnyHedge-powered application, as briefly mentioned above, and the production release followed in April 2023.
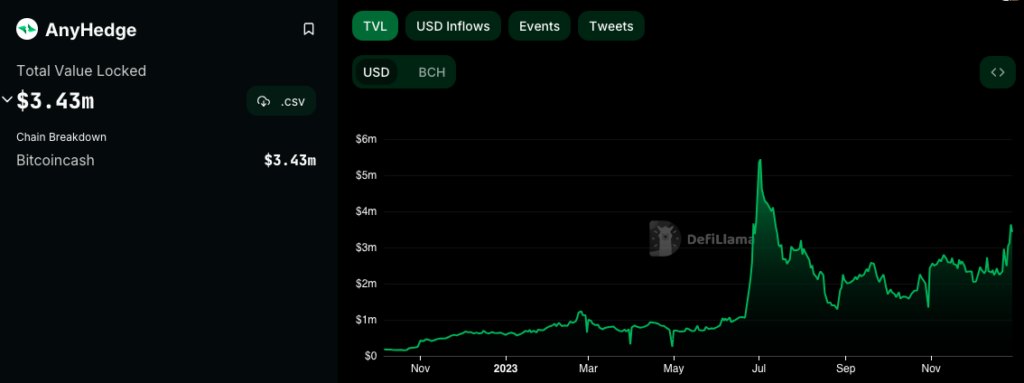
As previously mentioned, users on BCH Bull have the option to hedge the value of their Bitcoin Cash against another asset or take a leveraged long position on Bitcoin Cash relative to another asset. These contracts leverage oracles that supply authenticated price information for Bitcoin Cash against diverse assets. The specifics of the contract remain confidential until settlement, and all contracts are executed on-chain without the involvement of custodians. At the time of writing, the AnyHedge protocol, implemented via BCH Bull, showcases a substantial total value locked, exceeding $3 million USD worth of Bitcoin Cash, underlining its growing adoption and usage.
Following the CashTokens upgrade in 2023, TapSwap emerged as the leading NFT-trading platform on Bitcoin Cash, extending its functionality to include fungible token trading. Sellers have the flexibility to list any tokens at the prices of their choice, while buyers can conveniently browse through available sell orders, only incurring a minimal platform fee upon purchase. Notably, the entire platform operates on a non-custodial basis and offers seamless integration with Bitcoin Cash wallets, ensuring user-friendly access.
In 2023, the decentralized exchange (DEX) Cauldron unveiled its pre-release beta, establishing a significant presence in the Bitcoin Cash DeFi ecosystem. Distinguishing itself as the pioneer in non-custodial automated liquidity protocols, Cauldron allows users to seamlessly swap between BCH and CashTokens or contribute liquidity through micro-pools. Leveraging Bitcoin Cash’s 0-conf capabilities, Cauldron proudly claims the title of the world’s fastest swap contract, emphasizing speed and efficiency in decentralized trading.
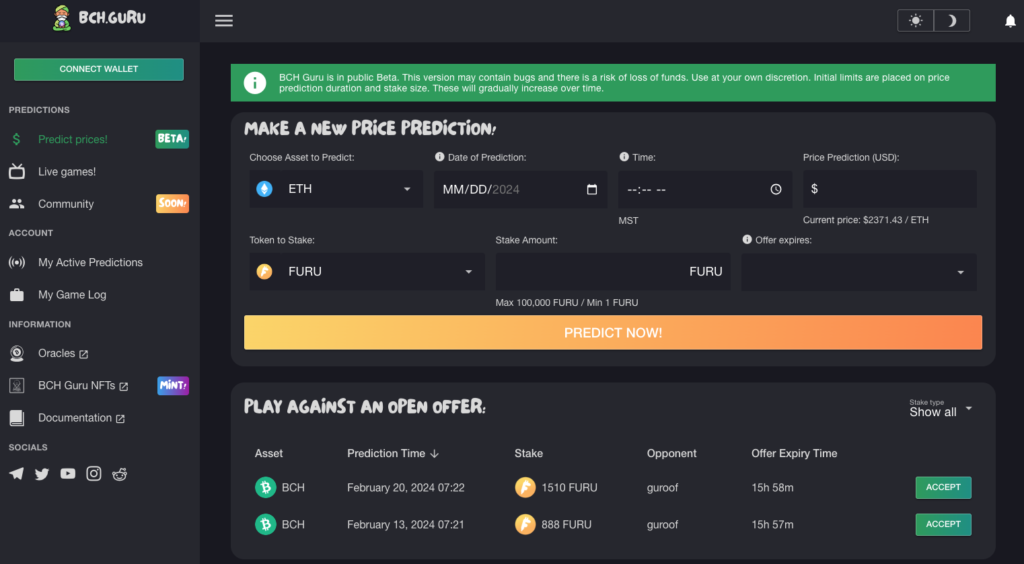
Emerging as a prominent contributor in the Bitcoin Cash DeFi arena, BCH Guru introduces a unique approach by intertwining NFTs with a price prediction app. The platform features a series of distinctive and collectible NFTs that actively contribute to the BCH Guru price prediction game. In its current beta phase, the app empowers users to stake Furu tokens – initially distributed to BCH Guru NFT holders – and engage in a player-vs-player (PVP) prediction game. Contestants predicting the closest Bitcoin Cash price at the game’s conclusion win the entire Furu token pot.
The beta serves as a precursor to the upcoming production version, which will extend functionality to Bitcoin Cash staking. All BCH Guru contracts are executed directly on the Bitcoin Cash blockchain, ensuring complete non-custodial security. While the initial PVP game sets the stage, BCH Guru anticipates introducing an array of games and features in subsequent releases.
Key Takeaway:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has become a transformative force in the cryptocurrency space, reshaping traditional financial services by providing decentralized alternatives. BTC, historically resistant to native DeFi, lacks dedicated infrastructure or options on its blockchain. Bitcoin Cash, after overcoming delays related to development and community direction, witnessed the introduction of native, on-chain DeFi. General Protocols introduced the AnyHedge protocol, offering a decentralized, collateral-based solution with secure, on-chain contracts – now implemented on BCH Bull. TapSwap, an NFT- and fungible token-trading platform; and Cauldron, a non-custodial automated market maker DEX further expanded DeFi options on Bitcoin Cash. BCH Guru innovates by combining NFTs with a price prediction app, offering a unique staking experience. These developments underscore the growing diversity and adoption of decentralized financial applications on Bitcoin Cash.
Privacy
The capacity to carry out transactions without relying on traditional intermediaries strengthens financial confidentiality. Since its inception, Bitcoin adopted a pseudonymous approach, ensuring transactions aren’t directly tied to specific identities. However, the system has consistently maintained an open ledger, allowing anyone to review transactions and potentially link identities through alternative channels. While this transparency is crucial for blockchain integrity, it poses a challenge in terms of privacy considerations.
In the face of prevalent data breaches and cyber threats, privacy becomes essential to shield against surveillance by government agencies and other malicious actors. The effectiveness of private transactions lies in safeguarding users from unwarranted surveillance, providing a layer of defense against censorship and unwarranted sanctions. Additionally, privacy plays a crucial role in preserving autonomy within the cryptocurrency sphere, affording users financial independence.
To explore these privacy principles in practice, a comparison between BTC and Bitcoin Cash can illuminate privacy approaches implemented in each coin and how confidentiality concerns are addressed. While many privacy options are available on both networks (e.g. hosting a full node, avoiding address reuse, etc), we will focus on the distinct approaches each coin has available.
Pricey Privacy
The most popular privacy applications on BTC utilize the CoinJoin method. CoinJoin, a prominent privacy-enhancing technique, involves the creation of a large BTC transaction that combines inputs from multiple users and produces multiple equal outputs. By doing so, it obfuscates the linkage between specific outputs and the respective participants, making it challenging for observers to trace ownership accurately. This inherent privacy feature of CoinJoin disrupts the heuristics commonly employed by chain analysis companies, offering a boost to the confidentiality of BTC transactions.
CoinJoin is accessible through various wallets like Wasabi, Samourai, and Trezor Suite. However, a significant drawback associated with using these services is the incurred cost. The principal limitation of BTC – a block size restricted to 1 MB – substantially contributes to network congestion. This congestion leads to transaction fees costing several dollars (USD), even during periods of low activity. In times of high network activity, these fees can surge to $50 or more. The transaction fee would be in addition to any service fee the particular CoinJoin implementation might require.
The anonymity set associated with a CoinJoin transaction may be limited. The size of the anonymity set is influenced by the number of equal outputs within a single transaction. When the anonymity set is insufficiently large, there is a risk that observers monitoring the blockchain could potentially narrow down possibilities and trace the flow of funds through a CoinJoin transaction. Enhancing the anonymity set is achievable through the incorporation of additional CoinJoin rounds; however, the feasibility of such a measure is constrained by high transaction fees, making this approach potentially cost-prohibitive.
Low-Cost Confidentiality
CashShuffle, a well-established, decentralized CoinJoin implementation for Bitcoin Cash, has been in use for several years. Like other CoinJoin protocols, it employs equal amounts, combines them in a large transaction, and redistributes the appropriate amounts back to users. Notably, CashShuffle distinguishes itself by incorporating a matching service, enhancing its usability compared to alternative implementations.

However, in recent years, CashShuffle has been largely overshadowed by a more potent and sophisticated mixing protocol.
Introducing an innovative approach to CoinJoin, CashFusion stands out as a fully decentralized solution. Unlike typical CoinJoin protocols that necessitate equal amounts, CashFusion accommodates outputs of varying sizes. Leveraging the principles of Combinatorics, CashFusion ensures an exceptionally high number of potential configurations (e.g., quintillions or more) after a mixing transaction. This complexity adds a formidable layer of security, requiring malicious actors to rule out an overwhelming number of possibilities to determine the true origin of funds.
Endorsed by a security audit conducted by Kudelski Security, CashFusion stands as an effective and secure service for financial obfuscation. With Bitcoin Cash’s notably low transaction fees, the continuous mixing and remixing of a user’s entire wallet balance incurs only minimal costs, amounting to just pennies per day. This practice results in an impenetrable anonymity set, affording users a heightened level of privacy and peace of mind.
Key Takeaway:
Privacy is a pivotal aspect of cryptocurrency transactions. While executing transactions without traditional intermediaries enhances financial confidentiality, the openness of the ledger presents privacy challenges. Amid increasing government intervention, the need to safeguard against surveillance becomes imperative. BTC privacy services rely primarily on the CoinJoin method, where a large transaction mixes funds from multiple parties and sends back multiple equal outputs, obscuring the linkage between specific outputs and participants, thus enhancing confidentiality. However, sufficient anonymity through this method often requires a high cost due to BTC’s block size limitation, leading to network congestion and high transaction fees. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash introduces CoinJoin variations like CashShuffle and the innovative CashFusion. The latter mixes funds and sends back outputs of varying size, leveraging Combinatorics to ensure an intricate layer of security. With an endorsement from a security audit, CashFusion provides an effective and economical service for continuous coin mixing, offering a more affordable and secure alternative for users.
Conclusion
BTC is seen as the king of the cryptocurrency ecosystem and is acknowledged for its historical appreciation in the savings realm. However, it faces challenges with high fees, particularly impacting its use cases as a currency. While proponents of BTC assert the coin’s primacy in digital finance, its resistance to native token standards and DeFi options severely limits its versatility.
Moreover, the reliance on CoinJoin for privacy introduces cost issues due to network congestion, making sensitive use cases more opaque and thus susceptible to surveillance. Despite these challenges, BTC so far remains a prominent store of value and very popular within the cryptocurrency space.
On the other hand, Bitcoin Cash distinguishes itself with superior functionality for cash use cases, driven by cost-effective transactions and innovative privacy solutions like CashFusion. While Bitcoin Cash is not seen as a store of value in the same realm as BTC, Bitcoin Cash introduces inventive strategies through BCH Bull, utilizing the AnyHedge protocol to stabilize value in various currencies and assets.
The implementation of CashTokens stands out as a monumental leap, providing an on-chain token protocol validated by miners and expanding the potential for diverse smart contracts. Bitcoin Cash embraces DeFi with solutions like BCH Bull, multiple DEXs, and other DApps; showcasing a more proactive approach than BTC. Privacy considerations are addressed through CashFusion, offering a decentralized and cost-effective alternative for confidential transactions. While facing challenges in historical returns, Bitcoin Cash presents itself as a dynamic and versatile cryptocurrency with notable strengths in various domains.
What does the future hold for these two currencies and the apparent competition between them? BTC remains steadfast in its pursuit of being a store of value, offering limited functionality beyond this role. In contrast, Bitcoin Cash has been proactive in scaling technology and introducing new features, pushing the boundaries of cryptocurrency capabilities, regularly resulting in new use cases.
The future trajectory of these currencies may hinge on the evolving perception of cryptocurrency on a global scale. If the prevailing view continues to perceive cryptocurrency merely as a novel toy or speculative asset, BTC’s singular focus on being a store of value might be challenging for Bitcoin Cash or any other cryptocurrency to surpass.
However, should there be a shift in the world’s collective mindset, the game could change substantially. If demand ever ramps up for a true digital currency that can replace and even significantly enhance current use cases provided by traditional currencies, Bitcoin Cash could emerge as a valuable contender and potentially ascend to a prominent position. The future dynamics of global perception and requirements will play a pivotal role in shaping the fate of these cryptocurrencies.
Explore the Full Series of
“What is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash?”
Stay in the loop – subscribe to receive instant notifications on our latest blog posts, delivered straight to your inbox